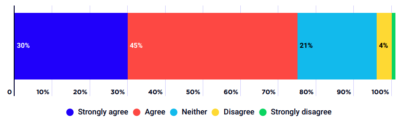
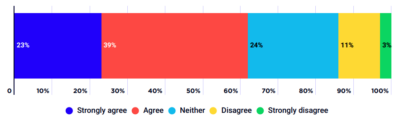
This graph shows the average annual growth in household after-tax incomes for each quintile from 1999-00 to 2017-18.
During this period, average annual growth for the highest 20% (after taking account of inflation), compared with 2.2% for the middle 20% and 2% for the lowest 20%. While this is the case, there were major shifts in income growth and distribution before and after the Global Financial Crisis (GFC) in 2008. During the boom years growth in high incomes suprassed that of middle and lower income households. The average after-tax incomes of the highest 20% rose from $2,581 per week in 1999-00 to $3,619 in 2087-08 (5%0 per year). This compares with an increase from $1,308 to $1,733 for the middle 20% (4.1% a year) and an increase from $519 – $680 for the lowest 20% (3.9% a year). The income of the highest 5% rose during the boom from $3,514 a week to $5,611 (7.5% a year). After the GFC, growth in household income generally flat-lined, along with the trend in income inequality.